This frequent pathology poses problems of public health, diagnosis, origin and finally treatment.
Diagnosis of fibromyalgia
Previously it was necessary to test by the pressure of the thumb from 11 to 18 points (The pressure must be exerted with a theoretical pressure of 4 kg, which in practice corresponds to a palpation which makes it possible to whiten the nail).
Diagnosis should include (American College of Rheumatology Recommendation 2016):
- Pain lasting for more than three months.
- A WPI (Widepread Pain Index) Score greater than or equal to 7 with a severity scald of 5 or
- A WPI score between 3 and 6 and a severity score of 9
The WPI Consists of counting the painful areas according to the following diagram:
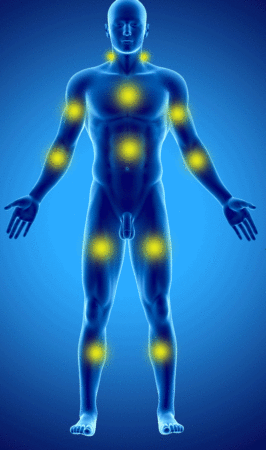
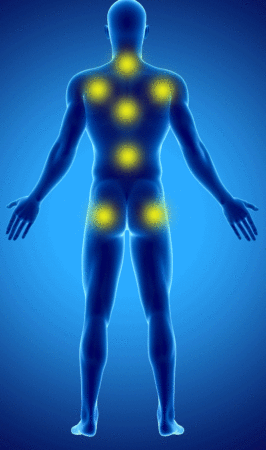
The week before the consultation, the patient counts the number of painful areas according to this diagram (from 0 to 19).
The symptom severity scale is performed as follows:
Symptoms are rated from 0 to 3 according to their severity (0: nothing, 1: little, 2: moderate, 3: strong or severe)
- Fatigue
- Sleeping troubles
- cognitive disorders
- Somatic disorders: 0 = no symptoms, 1 = few symptoms, 2 = moderate number of symptoms, 3 = many symptoms.
- Somatic symptoms to consider:
- Muscle pain,
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome,
- Muscular weakness,
- Headache,
- Abdominal pain/cramps
- numbness/tingling,
- Dizziness,
- Depression,
- Constipation,
- Pain in the upper abdomen,
- Nausea,
- Nervousness,
- Chest pain,
- Blurred vision,
Fever, - Diarrhea,
- Dry mouth,
- Itching,
- Wheezing,
- Raynaud’s phenomenon,
- Urticaria,
- Skin marks,
- Ringing in the ears,
- Vomiting,
- Stomach pains,
- Mouth ulcers,
- Loss or change of taste,
- Seizures (PNEC),
- Dry eyes,
- Shortness of breath,
- Loss of appetite,
- Eruption,
- Sun sensitivity,
- Difficult hearing,
- Bruises,
- Hair loss,
- Frequent need to urinate,
- Painful urination,
- Bladder spasms.
CAUTION ALL OF THESE SYMPTOMS CAN BE ENCOUNTERED IN OTHER PATHOLOGIES
| Painful areas | 0-19 | |
| Scale of severity | fatigue | 0-3 |
| sleeping troubles | 0-3 | |
| cognitive disorders | 0-3 | |
| somatic disorders | 0-3 | |
| Total | 0-31 |
A score greater than 13 is in favor of the diagnosis.
The symptoms are not related to another pathology (last criterion).
An initial assessment will look for known organic causes:
Additional tests :
They are useful to eliminate another cause.
NO ADDITIONAL EXAMINATION CURRENTLY ALLOWS TO MAKE THE DIAGNOSIS OF FIBROMYALGIA.
- Complete blood count
- Sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein (testing for chronic inflammatory disease is essential)
- Blood ionogram, calcium, phosphoremia, magnesium (hypokalemia, osteomalacia are eliminated)
- Urea, creatinine, uric acid (rule out renal failure or gout)
- CPK, aldolase (search for specific muscle damage)
- T3, T4, TSH (thyroid abnormalities are ruled out)
- PTH, Vitamin D
- Serum iron, Add to dictionary (an iron deficiency can be responsible for chronic pain).
- FAN, FR, anti-SSA and SSB antibodies
We will check the absence of drug intake responsible for muscle pain (statins for example)
Origin of fibromyalgia
The various studies on the subject are never formal, however in some of them we find:
- A decrease in cerebral serotonin
- An increase in substance P in the cerebrospinal fluid
- An anomaly in the regulation of peripheral arteriovenous shunts
- A decrease in the number of C fibers on skin biopsies
- A change in the sensitivity of the skin and muscles to pain and touch,
A ratio of 7 women for a man with this pathology.
Based on these studies and the presentation of patients, multiple theories have emerged in recent years:
Psychogenic origin
The disease would be a somatization of a psychic disorder or a psychic pain.
Central origin
This theory seems to be the most accepted at present, there would be a decrease in the influence of the pain inhibitor system which comes from the brain and reduces the transmission of the pain message by the spinal cord.
Peripheral origin
The altered functioning of the peripheral arteriovenous shunts would lead to “ischemia” (lack of oxygen) of the muscle and skin tissues responsible for pain. The decrease in the number of C nerve fibers in the subcutaneous tissue would cause the equivalent of a small fiber neuropathy.
Which seems improbable given the distribution of pain (small fiber neuropathy gives above all an attack in distality (feet, hands)).
Fibromyalgia treatment
All of the doctors dealing with this pathology seem to agree on the maintenance of physical activity and exercise rehabilitation are essential. The treatments are medicinal or not:
Non-drug treatments are preferred :
- Kinésithérapie
- Balnéothérapie
- Cure thermal
- Acupuncture
- Mésothérapie
The medical treatment:
They usually combine serotonin reuptake inhibitors (antidepressants) and variable dose tramadol. Sometimes treatment with L-Carnitine over 3 months can improve muscle pain. Drug treatment should be balanced based on benefits and side effects. Ketamine-based protocols are sometimes effective. (details for doctors)
The treatments are to be combined, their effectiveness varies depending on the patient and a personalized approach is necessary.
