Anatomical reminder
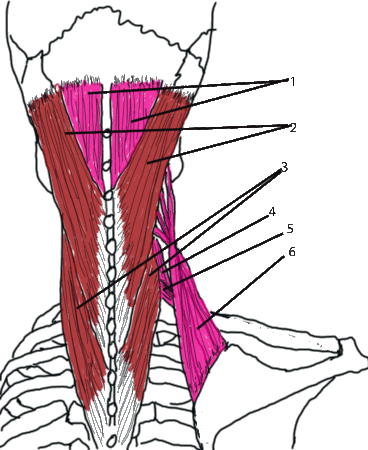
It is composed of an upper part, the splenius muscle of the head, and a lower part, the splenius muscle of the neck:
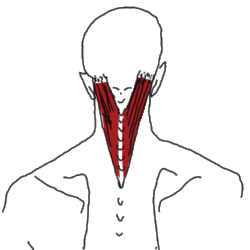
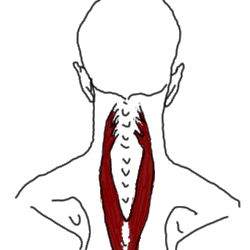
They lie directly under the trapezius muscle.
1- semi-spinous of the head.
2- Splenius of the head.
3- Splenius of the neck.
4- Middle scalene.
5- Posterior scalene.
6- Elevator of the scapula.
The innervation is done constantly by the roots C2 to C4 and sometimes by C1 and C5 in addition.
Both muscles are used for rotation and extension of the head and neck.
Myofascial Syndrome
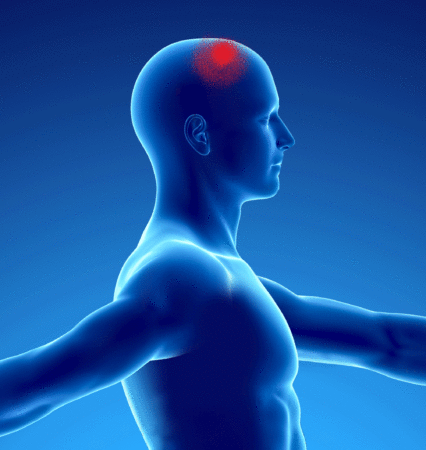
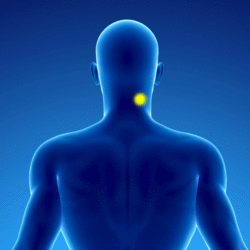
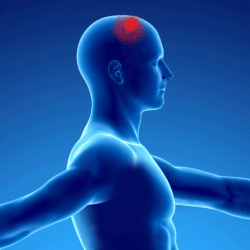
Patients presenting with a myofascial syndrome of the splenius of the head (in yellow on the underlying diagram) present pain referred to the vertex (in red on the underlying diagram):
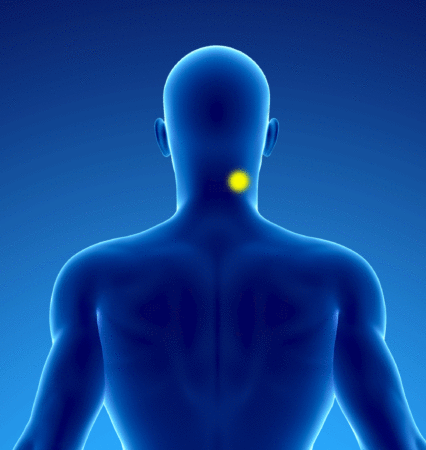
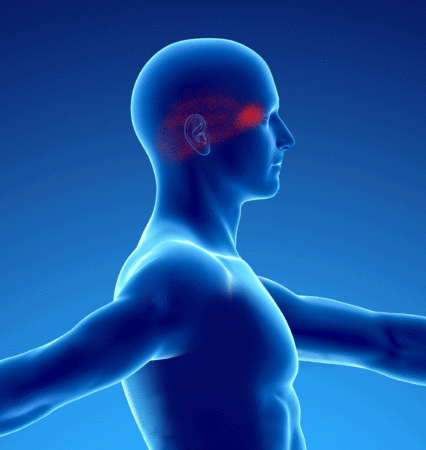
Patients with myofascial syndrome (in yellow) of the splenius of the neck have pain (in red) in the neck, skull and eye:
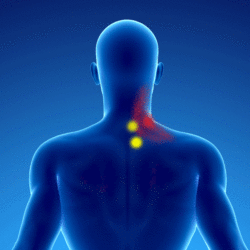
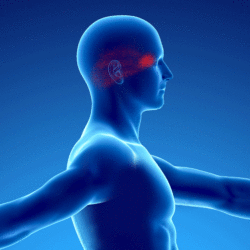
Positions of overexertion with the head forward or in rotation may be responsible. Typically this is a person working at a desk in front of a computer head leaning forward and facing the screen on the side.
Treatment
The treatment is essentially done by stretching with the head bent forward and in rotation.
Prevention is the best treatment, verification of vision and possible glasses, correction of body asymmetry. Wearing cold protection around the neck is also recommended.