Anatomical reminder
Muscle composed of 4 heads:
- Right femoral
- vastus medialis
- Vast Intermediate
- wide lateral

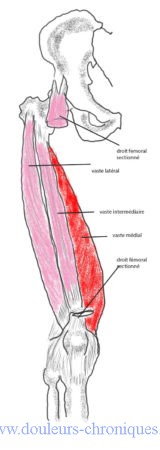
The muscles of the quadriceps group insert all 4, distally, on the patella. The patella is attached to the anterior tibial tuberosity by the patellar ligament.
The proximal insertion of the rectus femoris is on the antero-inferior iliac spine (left drawing in red). It is the only head of the quadriceps to cross two joints (hip and knee).
The proximal insertion of the vastus is done on the proximal part of the femur.
The quadriceps femoris acts as an extensor of the leg, but also as a flexor of the thigh on the pelvis through the rectus femoris. It stabilizes the knee when walking (maintenance of the patella in position by the vastus muscles, control of knee flexion), It participates in the anteroposterior movements of the trunk.
Myofascial syndrome of the quadriceps femoris muscle
The rectus femoris
Frequent myofascial syndrome, the responsible areas are often located in the proximal part of the muscle close to the hip but the referred pain is located at the level of the knee sometimes felt as deep. More rarely the trigger point is located in the lower part of the muscle, above the patella and in this case the pain is felt as deep or even intra-articular.
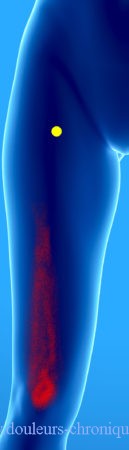
A poorly known cause of the appearance of this syndrome is repeated injection into the upper thigh of treatment by the subcutaneous route, for example in insulin-dependent diabetics or prolonged anticoagulant treatments.
Repeated use of the muscle during strength training or gymnastics may also be responsible.
A violent contraction during a false step in a hole, or a descent from the sidewalk can also trigger the syndrome.
Finally in certain orthopedic immobilizations, shortened muscle, this syndrome can also appear (for example treatment of a knee sprain, or rupture of cruciate ligaments)
The treatment is, as for this type of pathology, based on deep massages and stretching. Stretching is done by hyperextension behind the hip by bending the knee.
The vastus medialis
The most common trigger point of this muscle is in the distal part of the muscle.
The pain is dull in the part represented in red on the diagram below. For the trigger points located higher, a band pain on the antero-internal part of the thigh is described.

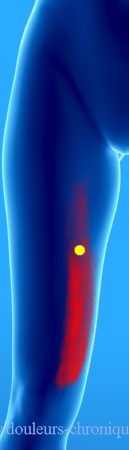
The particularity of the lowest trigger point is that it can lead to functional dysfunction without the appearance of associated pain. This functional gene results in a sagging knee with, sometimes, an associated fall.
This myofascial syndrome can be triggered by excessive pronation of the foot (mid-tarsal hypermobility, equinus foot, muscle imbalance, Morton’s foot, flat foot). It can also appear, when there is an inequality in the length of the lower limbs, in the shortest limb.
Sports activities such as jogging, skiing, football can also be responsible.
The position on the knees on hard ground can also maintain these pains (gardening, tiling, etc.)
The treatment is done by deep massages and stretching of the hip muscle in complete abduction and external rotation with the knee bent.
The vast intermediary
Referred pain related to trigger points of this muscle gives pain in the front part of the thigh, especially in its middle part.
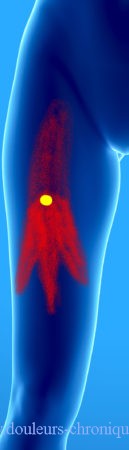
It should be noted that the diagnosis is more difficult because palpation of the muscle that lies under the rectus femoris is almost impossible.
Affected patients find it difficult to fully extend the knee, especially after being immobile for prolonged periods.
The treatment is done by stretching with the knee flexed to the maximum.
The vast lateral
There are many possible trigger points in this large muscle. Referred pain is on the side of the thigh and radiates up and down from the iliac crest to the knee depending on the pain location.
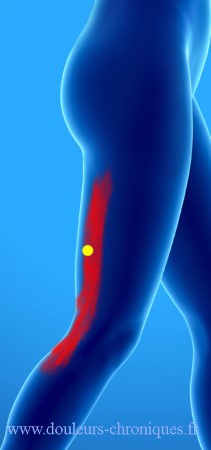
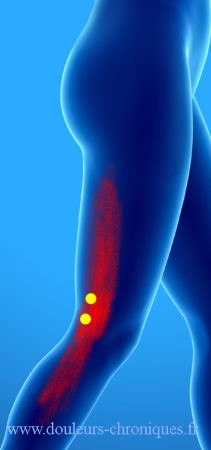
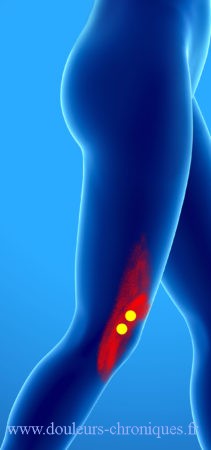
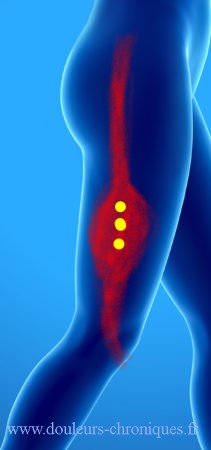
The lowest located trigger points give pain on the outer edge of the patella with sensation of a blocked patella.
These pains predominate during walking but also when the subject sleeps on the affected side.
Treatment is best done by ischemic compression. Especially with self-massages lying on your side on a tennis ball
