Reminder
- Explain chronic pain
- Cicatricial neuropathies
- Associated myofascial syndromes that modify the clinical symptoms of cicatricial neuropathies.
Description
Knee surgery is done either arthroscopically or by open surgery (knee prosthesis, tendon transposition intervention, ligamentoplasty, etc.). The different approaches are schematized below:
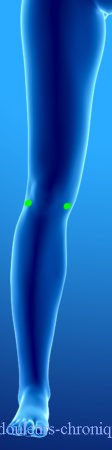
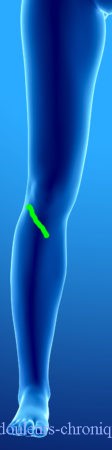
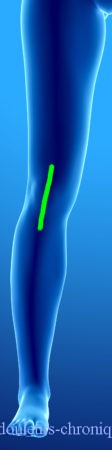
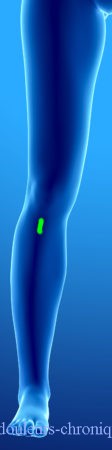
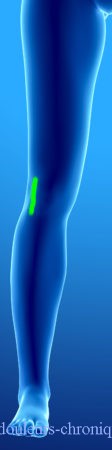
These different approaches can be responsible for chronic neuropathic pain. In general, these pains are localized in oil spots around the scarred areas and follow the main nerve innervation topography of the area (Femoral nerve and Sciatic nerve for the knee).
The attack can affect the nerves of pain, the nerves of superficial and deep sensitivity (in the case of lateral scars, balance disorders or even repeated ankle sprains can be seen), the motor nerves and the nerves of the autonomic nervous system. If all of these conditions are affected, the painful pathology described becomes CRPS type 1.
Below are examples of painful topographies found in patients:
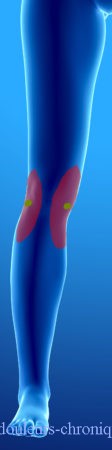
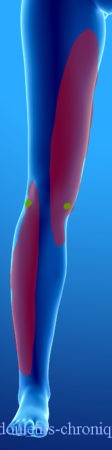
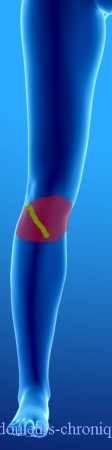
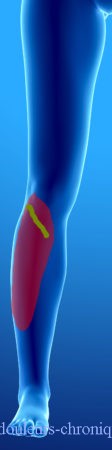
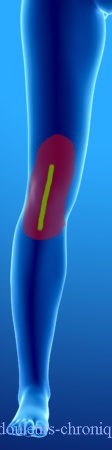
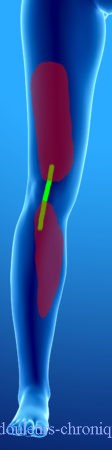
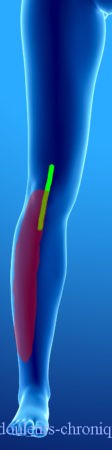
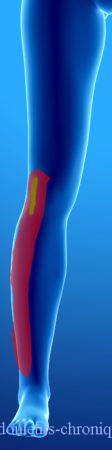
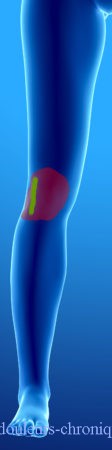
It should be noted that in the case of knee prosthesis (median scar) the patients also describe a feeling of bone pain and/or prosthesis “too big”.
In all of these painful pathologies, the diagnosis is made by the rolling palpation maneuver which triggers neuropathic-like pain.
